Should You DC Test Your Rubber Insulating Gloves?

Electrical safety in the workplace consistently ranks in OSHA’s Top 10 List of Most Commonly Cited OSHA Safety Violations. While LOTO (lockout-tagout) and arc flash assessments are certainly components of a comprehensive electrical safety program, only rubber insulating gloves (electrical gloves) protect working hands from electrical shock hazards. Hazards above 50 volts are recognized by OSHA in 1910.269 Working on Exposed Energized Parts, which includes the requirement that employees must avoid contact above 50 volts AC unless they are insulated with rubber insulating gloves meeting the ASTM D120 standard (per OSHA 1926.97).
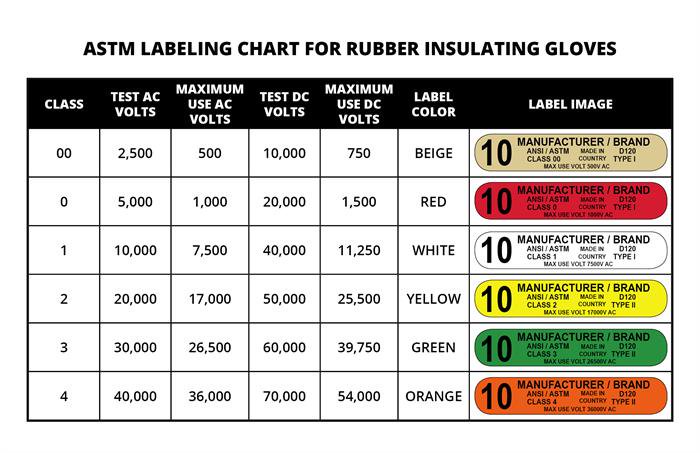
Since the late 19th century, electric power systems standardized on alternating current (AC). Since AC systems range from residential and commercial 110-volt power to ultra-high-voltage overhead power lines, all of the rubber insulating products covered by ASTM Specifications as referenced by OSHA are manufactured and tested with AC. These ASTM Specifications include not only testing voltages but maximum use voltages as well. While no laboratory test can perfectly simulate real world hazards and conditions, it makes sense to test with AC for use with AC.
 Even though electricity today is still predominantly powered by AC, computers, LEDs, solar cells, electrified mass transit and transportation, and electric vehicles all run on DC power. The ASTM Specifications for Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers generally include DC test voltages and DC maximum use voltages as well.
Even though electricity today is still predominantly powered by AC, computers, LEDs, solar cells, electrified mass transit and transportation, and electric vehicles all run on DC power. The ASTM Specifications for Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers generally include DC test voltages and DC maximum use voltages as well.
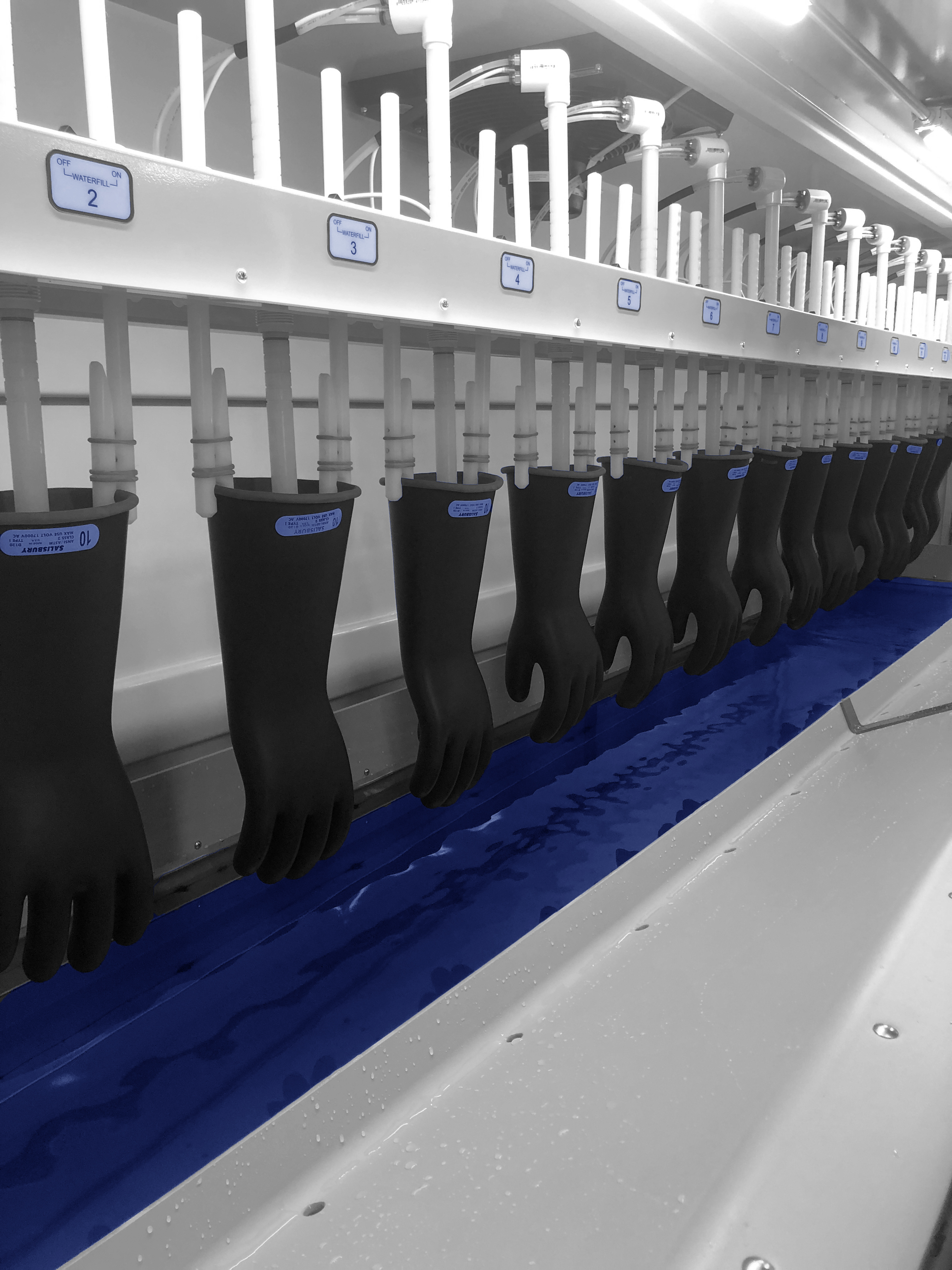
OSHA regulations and ASTM standards require regular dielectric testing of in-service electrical gloves in order to maintain compliance and ensure the products’ safety and integrity when exposed to a wide range of voltages. The interval between the date of issue and electrical testing should be based on work practices and test experience. For electrical gloves, the interval shall not exceed six months except for industries such as telecommunications that utilize electrical gloves as precautionary protection. However, do not place electrical gloves into service unless they have been tested electrically within the previous twelve months.
Periodic retesting of electrical gloves should be performed at the proof test voltage using specialized equipment designed to gradually increase the voltage to the desired test level. The dielectric test is two-fold: pass/fail on the ability to withstand the rated test voltage and, for electrical gloves, quantitative on the ability to prevent electric current from passing through the rubber goods above the maximum contained in the specifications. At a minimum, ASTM standards require that the inspection and testing process include the following steps:
- Check-in
- Removing previous testing marking
- Washing using cleaning agents that will not degrade the insulating properties
- Visual inspection of all surfaces (inside and out)
- Electrical testing
- Final inspection
- Recordkeeping
- Marking
- Packing in appropriate containers (“appropriate containers” means boxes, or similar sturdy packaging materials to prevent folding, creasing or similar loose storage that can cause stress on the rubber) for storage or shipment
![]() While AC (alternating current) testing is the primary method of electrical testing and applicable for general use, DC (direct current) testing is necessary for rubber insulating products in applications where there is exposure to DC. Moreover, the ASTM Specifications for Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers do include both AC and DC test voltages and maximum use voltages for safety. Therefore, it makes sense to DC test electrical gloves where there is exposure to DC energized circuits and equipment.
While AC (alternating current) testing is the primary method of electrical testing and applicable for general use, DC (direct current) testing is necessary for rubber insulating products in applications where there is exposure to DC. Moreover, the ASTM Specifications for Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers do include both AC and DC test voltages and maximum use voltages for safety. Therefore, it makes sense to DC test electrical gloves where there is exposure to DC energized circuits and equipment.
The Saf-T-Gard® Voltgard® Test Lab is the largest, independent NAIL4PET-accredited test lab for rubber insulating products in the United States and offers complete retesting and certification of rubber gloves, sleeves, blankets, line hose, covers, dielectric footwear, jumper cables, grounding sets, plastic guards, hot sticks, matting, hoods, and hand tools. The Saf-T-Gard® Voltgard® Test Lab is outfitted with state-of-the-art equipment for the complete testing of these products, including washing, visual inspecting, and electrical testing – all to applicable ASTM standards.
![]() The Saf-T-Gard® Voltgard® Test Lab proudly offers electrical testing at both AC and DC voltages. Products passing the inspection and test procedures can then be returned to service for continued use and cost savings over purchasing a new pair of electrical gloves that could have been re-tested and re-certified by a qualified test lab for a fraction of the cost. All electrical gloves are tested at AC voltages for general use and clearly marked with the AC maximum use voltage prior to shipment, and all electrical gloves tested at DC voltages are clearly marked with the DC maximum use voltage.
The Saf-T-Gard® Voltgard® Test Lab proudly offers electrical testing at both AC and DC voltages. Products passing the inspection and test procedures can then be returned to service for continued use and cost savings over purchasing a new pair of electrical gloves that could have been re-tested and re-certified by a qualified test lab for a fraction of the cost. All electrical gloves are tested at AC voltages for general use and clearly marked with the AC maximum use voltage prior to shipment, and all electrical gloves tested at DC voltages are clearly marked with the DC maximum use voltage.
Moreover, the Saf-T-Gard® Voltgard® Test Lab has one of the largest new rubber goods inventories available to immediately replace any goods not meeting applicable standards, including ASTM, OSHA, or your company’s own safety policies.
So why spend approximately $200 to replace a pair of electrical gloves when you can have them tested and recertified at the Saf-T-Gard® Voltgard® Test Lab for less than 10% of that cost without sacrificing safety or compliance?

